 "Weather By Giannetta" "Weather By Giannetta" |
|---|
 "Weather By Giannetta" "Weather By Giannetta" |
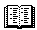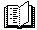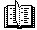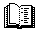
|---|
"Charles A. Giannetta"
|
|---|
 - "This page best viewed with "Microsoft Internet Explorer". Text Size "Smaller"
- "This page best viewed with "Microsoft Internet Explorer". Text Size "Smaller"
Picture 1024 X 768 - 17 or 21 inch Monitor
 - * * Gini & Charlie's Weather & Meteorology Glossary Page * * - - * * Gini & Charlie's Weather & Meteorology Glossary Page * * - 
A |B |C |D |E |F |G |H |I |J |K |L |M |N |O |P |Q |R |S |T |U |V |W
|X |Y |Z
|
|---|
"A"
A: Designated letter for an "Arctic Mass"
A: Designated letter for: "Hail"
Above Average: The departure from normal which is: The longterm average of an element (Temperature: Rainfall: Snowfall: Etc:) for a specific location.
Above Normal: The departure from normal which is: The longterm average of an element (Temperature: Rainfall: Snowfall: Etc:) for a specific location.
Absolute Humidity:The mass of water vapor (in grams) per unit volume of air containing the water vapor expressed as grams of water vapor per cubic meter of air.
Absolute Zero:-273 Degs on the Kelvin Temperature Scale.
AC: Convective Outlook Bulletin.
Acid Precipitation: Rain: Snow: Sleet: Which contain high levels and acid forming chemicals.
Acronyms:
Advection: The horizontal movement of air.
Aerovane: A weather instrument which indicates wind speed and direction.
"Air Mass & Weather Systems Nicknames"
1. Alberta Clipper: Low pressure weather systems that form on the eastern side of the
Rocky Mountains in the region of Alberta Province, Canada.
They move rapidy Southeast over the Eastern & Central United
States producung a low amount of snowfall in the winter and
a low anmount of rainfall in the summer due to the fact they
do not contain much moisture.
2. Pineapple Express: Is a series of moist weather systems which orginate near Hawaii.
Move Northeast and enter the Western United States from Washington,
south to the California Coast, producing heavy rainfall over this region
which in turn produce mud and land slides.
3. Siberian Express: An Arctic Air Mass which developes over the Arctic or near
Siberia, Russia. They contain extreamly frigid temperatures well
below zero and are fast moving. These air masses affect the
Eastern, Central & Southern United States with very low temperatures.
Airmass Thunderstorms: Thunderstorms which occur in air masses and are not as severe as frontal thunderstorms.
Anemometer: A weather instrument used to measure wind speed.
Altimeter:................A instrument onboard an aircraft, (Aneroid Barometer) calibrated to measure altitude in feet.
Aurora Australis: Southern Lights.
A |B |C |D |E |F |G |H |I |J |K |L |M |N |O |P |Q |R |S |T |U |V |W
|X |Y |Z
Back To Top OF Page
© 1998 - 2013 Charles A. Giannetta
Actual Time Of Observation: The time the last element of a weather report was taken.
Additive Data: Elements added to the remarks portion of a weather observation.
Adiabatic Chart:Chart used to plot upper air soundings in a graph form.
Adiabatic Lapse Rate of Dry Air:The dry adiabatic lapse rate of dry air is 5 Degs. F or 3 Degs. C. per 1,000 ft.
Adiabatic Lapse Rate of Moist Air:The moist adiabatic lapse rate is 3.0 Degs. F or 1.5 Degs. C. per 1,000 ft.
Adiabatic Process: The change in volume or pressure without the loss or gain of heat.
In the "Adiabatic Process" compression results in heating, expansion results in cooling.

Advection Fog:Clouds at ground level produced by cooling of warm humid air as it moves over a cooler surface.
Aerosol: Particals in the atmosphere such as smoke, salt, dust, sand.

Air: Air Above 1 acre weighs about 40,000 tons.
Air: A cubic foot of air at a temperature of 32 degs. F. weighs about 1 ounce.
Air: A person con only live about 10 minutes without air.
Aircraft Ceiling: The height of the base of the clouds observed and measured with an aircraft.
Aircraft Mishap: An aircraft accident or incident.
Air Discharges: Cloud to air lightning which do not hit the ground.
Airmet: Acronym for: Airman's Meteorological Information: Inflight weather advisory forecast
for possible hazardous weather conditions for inexperienced pilots or pilots flying light aircraft.
Air: Liquid: If air is cooled to about -315 Deg. F., it changes to a liquid called, (Liquid Air). It looks like water and pours like water.



Air Polluants: Primary: Chloro-Fluro-Carbons: Hair Sprays: Freon: Gasolene: CO2: Sulfur: Nitrogen: Carbon:
Air Polluants: Secondary: Acid Rain: Smog: Surlur Oxide: Nitorgen Oxide: Carbon Monoxide:
Airport Location: An aiport location shown as the latitude and longitude.
Air Pressure: Air pressure is equal on all sides.
Air Pressure: Air pressure is the same in and out of doors.
Air Pressure: Is measured with a "Barometer".
Albedo: The amount of radiation that is reflected from a surface expressed in percent.
Altimeter:
Altimeter Setting:
Altitude: The height above the ground.
Alto: Meaning high.
AM: Ante Merdiem: Before Noon
Anders Celsius: Born Nov. 27, 1701. Died April 25, 1744. A a Swedish astronomer.
 -
- 
Aneroid: Without liquid.
Aneroid Barometer: A portable weather instrument that uses a vacume chumber to measure air pressure.
Annual Rainfall: The amount of rain fall that occurs in a year over a specific area.
Anomally: A departure from normal over a period of time, such as temperature, rainfall, snowfall, etc.
Anomalous Propagation (AP) Due to temperature or moisture a radar beam is bent toward the ground
and produces false echos on the radar scope.
Anticyclone: High Pressure: Clock-Wise Air Flow: Desending Air:
Anticyclonic: High Pressure: Clock-Wise Air Flow: Desending Air:
Anthocyanins: Red & Purple colors in leaves.
Anvil Cloud: A cloud which forms at the top of a thunderstorm and is flattened out buy the wind and resembles an anvil.
AO1 Weather Station: AO1 is an automated station without a precipitation sensor.
AO2 Weather Station: AO2 is an automated station with a precipitation sensor.
Aphelion:The time of year when the Earth's is farthest from the Sun, around July 4.
Archive: A permenent record of weather observations.
Arctic Air Mass:Arctic "A": An extremely frigid and dry air mass that forms over the Arctic, Greenland and North America.
ARTC: Acronym for: Air Route Traffic Control Center.
Artesian Well: A well drilled with enough water pressure to flow without a pump.
ASOS:Acronym For: Automated Surface Observing Systems.
Astronomical Twilight: When the sun is no more than 18 Degs. below the horizon before sunrise and after sunset.
Atmosphere: The body of air which surrounds the earth which includes the troposphere, the lowest portion of the atmosphere in which we live.
Atmosphere: The maximun amount of moisture the atmosphere can hold is 4 percent.
Atmosphere: On average, residence time of water vapor in the atmosphere is about 10 days.
Atmosphere: Contains 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 1% rare gases of Argon/Carbon Dioxide/Neon/Helium/
Methane/Krypton/Nitrous Oxide/Hydrogen/Ozone and Xenon.
Atmospheric Ducting: A phenomenia which increases the range of electromagnetic waves such as radio...radar waves produced by
temperature inversions in the troposphere, the lower portion of the atmosphere
Atmospheric Optics: Phenomenia such as: Rainbows: Halos: Glories: Mirages:
Atmospheric Pressure: The pressure exerted by the atmosphere.
Atmospherics: Interference to radio and TV communications caused by electrical storms.
Atom:An atom is the smallest part of an element that has the properties of that element.
Attenuation: In Radio: TV: Radar: Sound: A reduction in power.
 Aviation Weather Definitrions:
Aviation Weather Definitrions:
Altimeter Setting:..The value to which the altimeter is set to indicate true altitude at the airport elevation.
Density Altutude:...The altitude in the standard atmosphere where the density is the same.
Flying Altitude:.......When air is colder than standard the altimeter indicates higher true altitude.
Flying Weather:.......When air is warmer than standard the altimeter indicates lower true altitude.
Indicated Altitude:..The altitude above MSL indicated on the altimeter when set to a local altimeter setting.
Pressure Altitude:..The altitude in the atmosphere where the pressure is the same.
True Altitude:.........The actual altitude above "Mean Sea Level".
Airmet:...........Acronym For: "AIRman's METeorological information for pilots of light aircraft,.
FA:..................Area Forecasts:
FT:..................Aviation Forecasts.
METAR:.........Routine scheduled weather observations.
NE:..................On a Radar Chart: No Echoes:
PIBAL:............Pilot Balloon.
Pirep:..............Pilot Report.
RADAT:..........Freezing Level.
Prevailing Visibility:.........Visibility over 1/2 of the horizon circle.
RVR:........................Runway Visual Range:
Sigmet:...................Acronym For: Significant Meteorological Forecast issued for hazardous weather.
Special Obs:..........Observations taken by desiganted weather stations for various weather changes such as: Tstorms: Hail: Wind: Visibility: ETC.
Synopic Obs:.........Observations taken by desiganted weather stations at 0000, 0600, 1200, & 1800 UTC.
TAF:...........Acronym For: Terminal Aerodrome Forecasts.
TWEB:.......Transcribed Weather Enroute Broadcast.
TWEB:.......Transcribed Weather Enroute Broadcast.
Aviation Weather:
IFR:Instrument Flight Rules.
IFR Weather Conditions: Ceiling less than 1,000 ft. and/or visibility less than 3 miles.
Marginal VFR Weather:Marginal Visual Flight Rules.
Marginal VFR Weather: Ceilings greater than or equal to1,000 ft. to less than or equal to 3,000 ft. and/or
VFR: In flying: Visual Flight Rules
VFR Weather: Ceiling greater than3,000 ft. and visibility greater than 5 miles.
Aurora Borealis: Northern Lights.
Automated Weather Report: A weather observation (REPORT) taken by an automatic weather station.
Automatice Surface Obeserving System: A project by the National Weather Service: Federal Aviation Administration: Department of Defense:
The U. S. primary surface weather observing network.
Autumn: The time of the year between summer and winter.
Autumn Equinox: Occurs on or about September 21.
Avalanche: Falling rock or snow and ice down a mountain side.
Average Max Temperature: The average of the High temperatures over an extended period. EXM. 12hrs. 24hrs. Month, Years.
Average Mean Temperature: The average of the High & Low temperatures over an extended period. EXM. 12hrs. 24hrs. Month, Years.
Average Min Temperature: The average of the Low temperatures over an extended period. EXM. 12hrs. 24hrs. Month, Years.
AWC: Acronym For: Aviation Weather Center
AWIPS: Acronym For: Advanced Weather Interactive Processing Systems.
AWOS: Acronym For: Automated Weather Observation System.
Azimuth: A direction in a circle of 360 degrees. Example: North = 360 Degs. Azimuth. East = 090 Degs. Azimuth
South =180 Degs. Azimuth. West = 270 Degs. Azimuth
Azore High: High Pressure which is located near the Azores in the winter and spring.
 - * * Gini & Charlie's Weather & Meteorology Glossary Page * * -
- * * Gini & Charlie's Weather & Meteorology Glossary Page * * - 
Have Fun!!
Have Fun!!
| Weather Glossary...WEATHER BY GIANNETTA,Giannetta,Charles,WA3RSQ,EL-NINO,Weather,Magazines,Meteorology,Hurricanes, Tornadoes,Floods,Clouds,Radar,Forecasting,Thunderstorms,Lightning,Atmosphere,69,Grand,Prix, WXDATA,Bath,Pa,USA,CD ROM,Weather,Disk,Meteorology,Graphics,Research,weatherbygiannetta.com |
|---|