 "Weather By Giannetta" "Weather By Giannetta" |
|---|
 "Weather By Giannetta" "Weather By Giannetta" |
|---|
"Charles A. Giannetta"
|
|---|
 - "This page best viewed with "Microsoft Internet Explorer". Text Size "Smaller"
- "This page best viewed with "Microsoft Internet Explorer". Text Size "Smaller"
Picture 1024 X 768 - 17 or 21 inch Monitor
 - * * Gini & Charlie's Weather & Meteorology Glossary Page * * - - * * Gini & Charlie's Weather & Meteorology Glossary Page * * - 
A |B |C |D |E |F |G |H |I |J |K |L |M |N |O |P |Q |R |S |T |U |V |W
|X |Y |Z
|
|---|
"T"
Temperature Scales:
1. Celsius Scale: Invented by Swedish Astronomer Andres Celsius: 1742
2. Fahrenheit Scale: Divised by German Physicist, Gabriel Daniel Farenheit: 1709.
3. Kelvin Scale: Invented by the Mathematian and Physicist: Sir William Thomson, Baron Kelvin of Largs, Lord Kelvin of Scotland: 1848.
4. Rankine Scale: Devised bt the Scottish Engineer & Physicist William John Macquom: 1859.
Terrestrial Radiation: Infrared radiation emitted by the earth.
"Thermos Bottle"
Thermals: Rising air currents.
Thin Obscuration: When 1/2 or more of the sky is obscured by surface based: Fog: Rain: Snow: Smoke: Etc.
1. Thunder: A low sound produced by lightning: Produced by the rapid expansion of air from the intense heat of lightning discharge.
Thunderstorm: A mesoscale weather system with thunder & lightning that reach heights to
60'000+ feet into the stratosphere.
"Thunderstorms"
1. Tstorms: About 40K-50k each 24 hrs. mostly over equator.
2. Tstorms: Cumulonimbus name give to tstorm cloud "CB"
Cumulus meaning Puffy. Nimbus meaning rain
3. Tstorms: During the disipating stage only the downdraft is present.
4. Tstorms: During The mature stage the up & dowdraft are present.
5. Tstorms: During the 3rd stage (Disipating) the tstorm has begun to die.
6. Tstorms: Duration. 1 to 24 hours.
7. Tstorms: Freezing Level. 32 Degs. F.
8. Tstorms: Gust Front.
9. Tstorms: Hail. Hail Shaft: Hail Streak.
10. Tstorms: Hail: One of the largest hailstone fell in
Nebraska in 1928. It was 17 inches around & weighed 1.5 lbs.
11. Tstorms: Hail Size: Gulfball. Baseball. Grapefruit.
12. Tstorms: Hail size: Pea, 1/4 in. Marble 1/2 in.
13. Tstorms: Hail: Sometimes there are 25 layers of large hailstone.
14. Tstorms: Inbedded. Clusters. Merging. Multicell.
15. Tstorms: Isolated : Extremely small no. Few 15% or less of area/line.
Scattered 16% to 45% of of area/line. Numerous 45%+ of area/line.
16. Tstorms: Light: Moderate: Severe:
17. Tstorms: Macrobursts: A downburtthat affects a path on the ground longer than 2.5 miles.
18. Tstorms: Mesocale" A down burst that affects a path on the ground shorter that 2.5 miles.
19. Tstorms: Millions of lightning strikes each hour.
20. Tstorms: Movements and wind speeds.
21. Tstorms: Occur Daytime or Nighttime: Anytime.
12. Tstroms: Occur in 3 stages. Cumulus. Mature. Dissapating.
23. Tstorms: On earth 2,000 tstorms occur each hour.
40K-50k each 24 hrs. mostly over equator.
24. Tstorms: Produce Downbursts:
25. Tstorms: Produce heavy amounts of rainfall.
26. Tstorms: Produce A scarf and anvil cloud at the top.
28. Tstorms: Release latent heat to the atmosphere.
29. Tstorms: Roll Cloud produuced in the fron of the storm.
30. Tstorms: Temperatures: Falling.
31. Tstorms: Severe Thunderstorm Warning. 1 hr. NWS.
32. Tstorms: Severe Tstorm: 50 mph wind. 3/4 in hail.
33. Tstorms: Squall Lines. Very Violent WX. Check Valve
34. Tstorms: Supercells to 60K ft. & may last 24 hr.
35. Tstorms: Tornadoes: South West side of Severe Thunderstorm.
36. Tstorms: Training Effect: One after another moving in the same direction.
37. Tstorms: Tstorms reach up to the stratosphere 50k to 60,000 ft. Rise above the tropopause.
38 Tstorms: Up & down drafts can reach speeds as fast as 200 mph
39. Tstorms: Stage 1. Cumulus:
40. Tstorms: Stage 2. Mature.
41. Tstorms: Stage 3. Dissipating.
Total Time Of Sunshine: The amount of time sunlight was detected.
"Tornado"
1. Tornado: About 10 a year occur in Pa.
2. Tornado: About 1100 occur each yr. and in every state.
3. Tornado: Are in the "Microscale Wind System" 0-5 scale.
4. Tornado: Causes: Strong vertical "Vortices" Vertical Suction.
5. Tornado: F Scale: Dr. Fujita: U. Of Chicago.
6. Tornado: Funnel Cloud is a tornado aloft not touching the ground.
7. Tornado: If caught in a tornado seek shelter indoors in the center
of the basement. In a mobile home in a small closet or area.
Get out of your car seek shelter. If caught outdoors find a
low spot. Lie down covering your head.
8. Tornado: Knock down just about anything in their path.
9. Tornado: Mobile homes. Large Buldings. Churches.
10. Tornado: Occur on the Southwst side of severe tstorms.
11. Tornado: Paths. Usually southwest to northeast.
12. Tornado: RADAR: NEXRAD: Net Genmeration Radar.
13. Tornado: Spin at speeds of 100 to 300+ mph.
14. Tornado: Spin CCW & CW. Can have more than 1 at a time.
15. Tornado: Stay on the ground for short & long distances.
16. Tornado: A tornado is dectected by Doppler Radar.
17. Tornado: Tornado Alley: Midwest US.
18. Tornado: Tornado Watch/Warnings Issued issued by the NWS.
19. Tornado: Waterspout: Tornado are over water.
20. Tornado: A funnel cloud which touches the ground.
21. Tornadic Activity: When a Tornado/Funnel Cloud or Waterspout may occur
or has been sighted.
Tropical Air: Air which froms over the tropics.
Tropics: An area on the earth located between the Tropic Of Cancer (23.5 Degs. N. Lat.) and The Tropic Of Capricorn (23.5 Degs. S. Lat.
T Designated letter for thunderstorm.
TACAN: Tactical Air Navigation System.
Tail Wind: When the wind is to your back.
Temperature: Air:The temperature of the "Dry Bulb" "Wet Bulb" & the "Dew Point" are the sme when the relative humidity is 100 percent..
Temperature: The hotness or coldness of a substance.
Temperature Of The Dry Bulb/Wet Bulb & Dew Point: Are the same when the relative humidity is 100 percent.
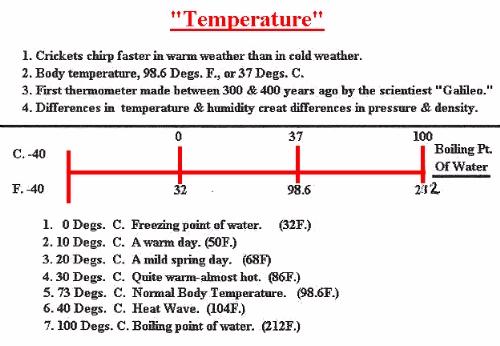
Temperature Scales: Fahrenheit Scalewhere 32 Degs. is freezing & 212 degs is boiling.
Centigrade Scale where 0 Degs. is freezing and 100 degs. is boiling.
Kelvin Scale: Where +233 degs. is freezing, 313.15 degs. is boiling. -273.15 Degs. is Absolute.
 -
-  -
-
Terminal Velocity: The speed at which the friction from the atmosphere equals the pull of gravity on an object.
Theodolite: A weather instrument similar to a surveying instrument which has elevation and
azimuth angle indicators, and is used to track weather balloons.

Thermograph: A weather instrument used to record temperature.

Three Phases of Water:Solid, Liquid & Gas.
2. Thunder: Can be heard from about 10 miles.
3. Thunder: Is the rapid expansion of the air molecules.
4. Thunder: Sound travels about 1,100 ft. per sec.
5. Thundersnow: Snow with a thunderstorm.
 -
- 
"Thundersorms: "Embedded" "Thunderstorms: Clusters"
1. Embeded thunderstorms are very hazardous to aviation. | 1. Mesoscale Convective Complex (MCC) remains nearly
2. These thundestorms are hidden in a large are a of | stationary and is in an area of numerous thunderstorms
precipitation and sometimes cannot be seen. | in an almost circular cluster.
3. If your aircraft has radar they can be detected by the| 2. The thunderstorms are interactive and cover a very
radar most of the time. | large area and sometimes the size ot the state of Pa.
4. If you do not have radar on board try to fly around | 3. These areas of thunderstorms move very slow and may last
these area, better yet, remain on the ground until the| for well over 12 hours.
weather system has moved on. | 4. The "MCC" is not associated with fronts and forms at
5. The tops of these areas may be to high to fly over. | night in the summer and contains very large amounts
These areas of embedded thunderstorms can produce | of rain.
high winds, severe turbulence, lightning, hail and | 5. "MCCs" occur mostly over the midwest and eastern
wind shear. | United States.
6. Stay least 20 to 30 miles from these areas and any |
thunderstorms. |
7. Always get the latest briefing about current and |
forecast weather conditions along your route and and |
at alternate terminals. |
"REMEMBER: SAFETY FIRST'

Time: AM=Ante Merdiem: Before Noon: - PM=Between Noon & Midnight.



Tipping Bucket Raingauge: A weather instrument that is used to measure precipitation in portions of 0.01 inch
that has a device that fills, tips and emptys.
Tornado: A small mass of air which whirls rapidly around a vertical axis with winds
of 100 to 300+ mph.
Tornado Watch: A Tornado is possible:
Tornado Warning: A Tornado has been sighted or was indicated on the NXRAD RADAR.

"Tornado Alley"
Tower Cumulus: A term given to cumulus clouds with great vertical height.
Tower Visibility: The prevailing visibility reported from an airport traffic tower.
Townsend Support: A metal support whichs hold the maximun & minimum thermometers.
TR Switch: Weather Radar Transmit/Receiver Switch which switches between transmit and receive modes.
Trace Of Precipitation: Less than .01 inch.
Trace Of Snowfall: Less than .1 inch.
Transmissometer: An instrument for determiming runway visibility located at the end of an airport runway.
Transpiration: When water in plants is transfered to a vapor into the atmosphere.
Triple Point: Point of occlusion where the occluded, cold and warm fronts come together.

Tropical Air Mass: A larger body of air which froms over the tropics that is warm and humid.
Tropical Cyclone: A cyclone which forms over the tropics.
Tropical Depression: The beginning stage of a "Hurricane" with wind speeds of at least
39 mph or 63 km. Given a number. Example: Tropical Depression No. 1.
Tropical Storm: A Tropical Cyclone having winds between 39 to 73 mph or 63 to 118 km. Given
a name starting with the letters "A" through "Z". Example: Tropical Storm "Art".
Tropical Storm Watch: Issued when there is threat of a tropical storm within 36 hours.
Tropical Storm Warning: Issued when there is threat of a tropical storm within 24 hours or less.
Tropic of Cancer: Located at 23'27" North Latitude.

Tropic of Capricorn: Located at 23'27" South Latitude.

Troposphere: The lowest portion of the atmosphere up to the tropopause. Varies in height from 60,000 feet at the equator to 40,000 feet over the poles.
Troposphere: The lowest portion of the atmosphere in which most weather occurs.
Tropopause: Varies with height from over 60,000 feet along the equator to 40- 45,000 feet above the poles.
Tropopause: An area of transition between the troposphere and the stratosphere. Varies with height from over 60,000 feet along the equator to 40- 45,000 feet above the poles.
Trough:A elongated area of low pressure on a weather map associated with a an area of low pressure.
True Wind Direction: Which way the wind is blowing from in relationship to true north.
Tsunamis: Giant ocean waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruption.
Turbulence: A disturbed flow of air in the atmosphere.
TWEB: Acronym for: Transcribed Weather Broadcast: A radio broadcast for pilots for self briefing prior to a flight.
Twilight: 1/2 hour before sunrise. 1/2 hour after sunset.
Twilight: Astronomical: When the sun is no more than 18 Degs. below the horizon before sunrise and after sunset.
Twilight: Civil: When the sun is no more than 6 Degs. below the horizon before sunrise and after sunset.
Twilight: Naurical: When the sun is no more than 12 Degs. below the horizon before sunrise and after sunset.
Twister: Tornado or Cyclone.
Typhoon: Another name given for a "Hurricane in the "Pacific Ocean".
 -
- 

"Super Typhoon Haiyan"
More text to come...

"The Human Ear"
More text to come...
© 1998 - 2013 Charles A. Giannetta
| Weather Glossary...WEATHER BY GIANNETTA,Giannetta,Charles,WA3RSQ,EL-NINO,Weather,Magazines,Meteorology,Hurricanes, Tornadoes,Floods,Clouds,Radar,Forecasting,Thunderstorms,Lightning,Atmosphere,69,Grand,Prix, WXDATA,Bath,Pa,USA,CD ROM,Weather,Disk,Meteorology,Graphics,Research,weatherbygiannetta.com |
|---|